Dogs love to explore the world with their mouths, making it crucial to properly care for your four-legged friend’s teeth. Learn more about the correct dental care for your dog here.
How Gum Problems Develop
When your dog eats, he ingests a multitude of bacteria with his food. Over time, these bacteria accumulate, particularly in the interdental area near the gums. Food particles tend to linger there after eating, providing sustenance for the bacteria.
Gradually, these bacteria, along with food remnants, form a sticky white layer known as dental plaque. If not removed, this plaque transforms into brownish-yellow tartar. These hardened deposits severely impact the gums and surrounding tissues, leading to inflammation. When the bacteria within the tartar attack the tooth’s hard substance, it results in cavities.
Consequences of Neglecting Dental Care for Dogs
Neglecting dental care for your dog can have severe consequences. Failure to clean your dog’s teeth can lead to diseases and serious inflammations in the mouth. Affected dogs often exhibit the following signs:
Pain:
Gum inflammation (gingivitis) due to plaque or tartar can be very painful for dogs. Inflammations can spread extensively under the gums, causing gum recession and damage to the tooth-supporting apparatus.
Chewing Difficulties with Poor Dental Care:
If your furry friend is experiencing tooth pain, it can affect his eating habits. He may either refuse to eat altogether or chew his food more cautiously. If bacteria have penetrated deeper tissues, leading to an abscess, chewing can become even more challenging.
Bad Breath:
Bacteria in plaque or tartar break down food residues, producing volatile sulfur compounds (VSCs). These compounds are notorious for their unpleasant smell and can cause bad breath in dogs.
Bacterial Infections:
If bacteria manage to enter your dog’s bloodstream, they can cause inflammation in other organs. Dental problems are often linked to conditions such as endocarditis (inflammation of the heart valves) or nephritis (kidney inflammation). In severe cases, it can lead to sepsis, a life-threatening condition for your furry companion.
Why Dental Care for Dogs Is Essential
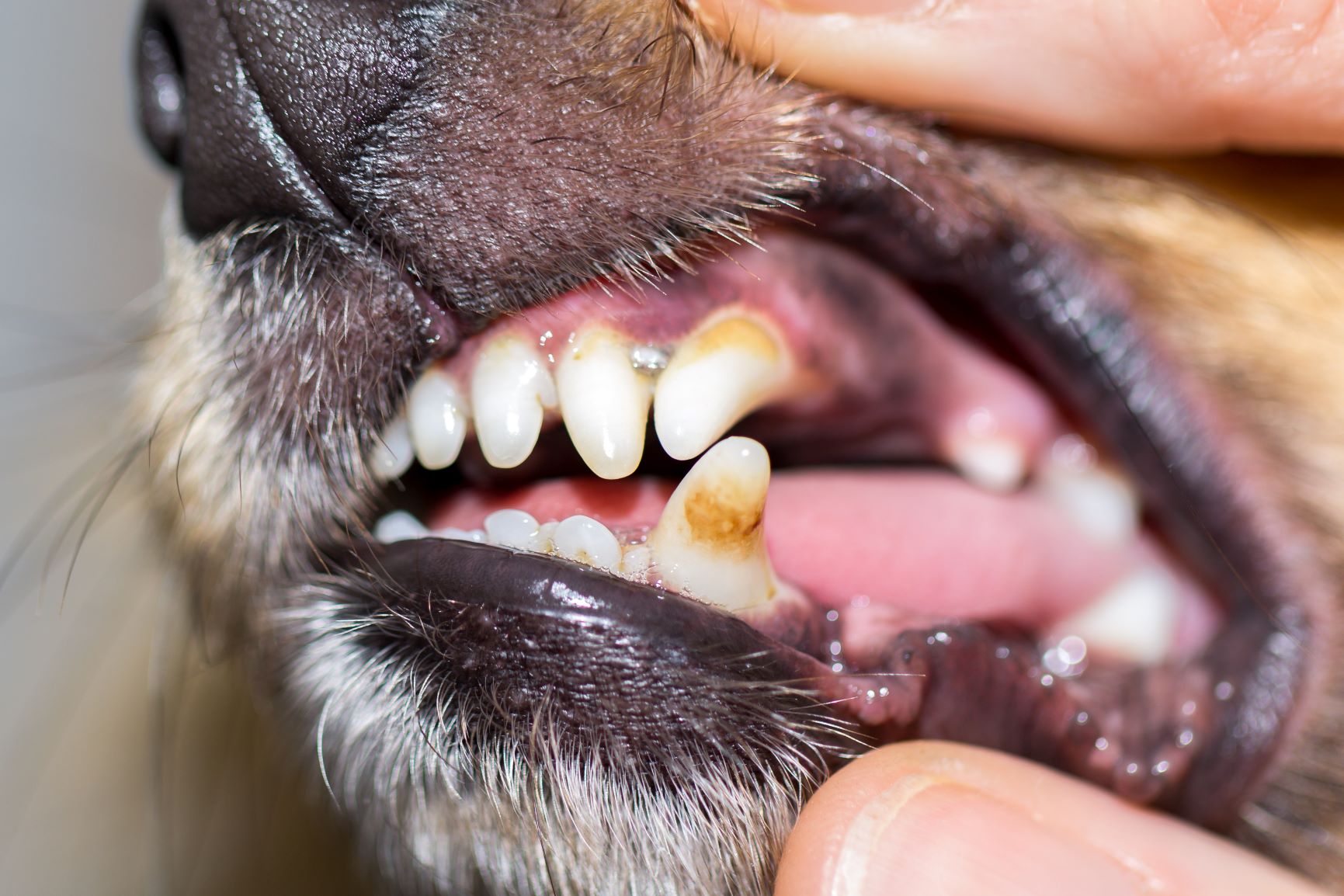
Numerous independent studies have examined the prevalence of gum diseases in dogs. These studies reveal that the gums of approximately four out of five dogs over three years old have already undergone pathological changes. Consequently, a significant portion of older dogs experiences severe gum problems.
Dogs use their teeth not only for chewing but also for lifting and moving objects. Your dog’s teeth are as crucial to him as your hands are to you. Given the extensive use of their teeth, regular dental care for dogs is indispensable.
Proper Dental Care for Dogs
The more often you clean your dog’s teeth, the less tartar will accumulate. Daily dental care is the best foundation for maintaining healthy canine teeth.
To ensure healthy teeth for your dog, combine the following measures for dental care:
Brushing Teeth:
Regularly brush your dog’s teeth using a canine toothbrush. This helps remove coarse food particles between the teeth. Special dog toothpaste aids in combating unpleasant breath and makes tooth brushing more palatable for your furry friend. Reward your dog after each cleaning session to help him get accustomed to the process.
Regular Veterinary Checkups:
Despite adequate dental care, some dogs may have a propensity to develop significant tartar. If your dog is prone to this, make sure to have regular veterinary checkups in addition to routine dental care.