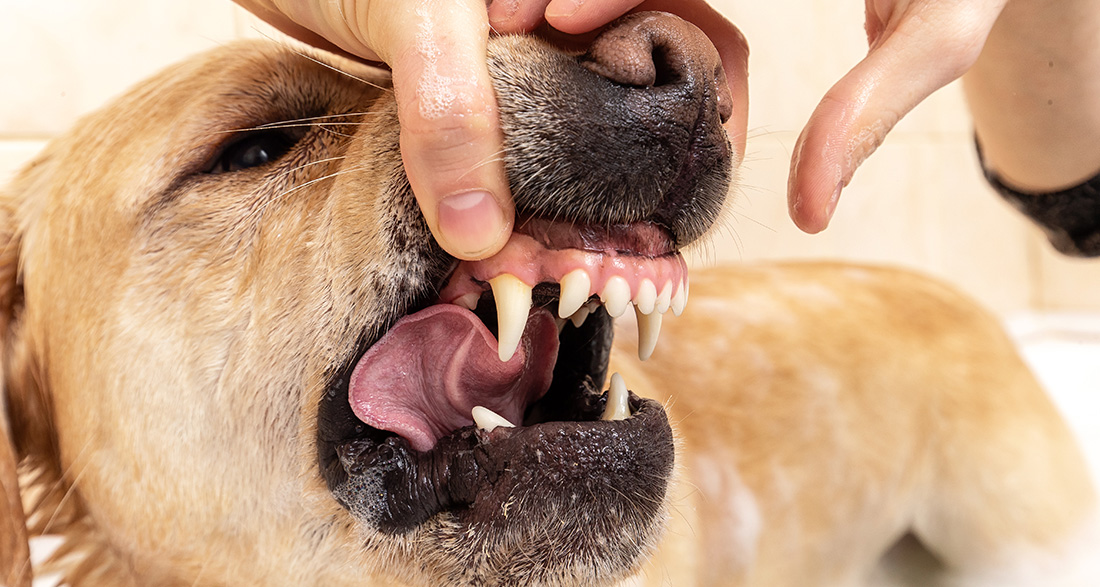
Gum inflammation can be truly painful for your dog. However, if you recognize the condition early and act quickly, you can usually keep it in check effortlessly. We’ll tell you what indicates gum inflammation in dogs, how to combat it, and how to prevent it in the long run.
Gum Inflammation in Dogs – How do I recognize it?
Detecting early gum inflammation in dogs is often challenging. Typically, there are no visible signs at first. Initially, strong bad breath is the only indication. If the inflammation goes unnoticed, the symptoms worsen, and your dog’s behavior and appearance will clearly indicate gingivitis.
The following symptoms may indicate gum inflammation:
- Your dog has extreme bad breath.
- He scratches his mouth with his paw.
- His gums are red and swollen.
- He chews on one side only.
- His saliva is purulent and bloody.
- He eats significantly less and loses weight.
- Dry food and chew treats are ignored.
- He growls at his food.
- His tooth necks are exposed, and the teeth are loose and falling out (in advanced gingivitis).
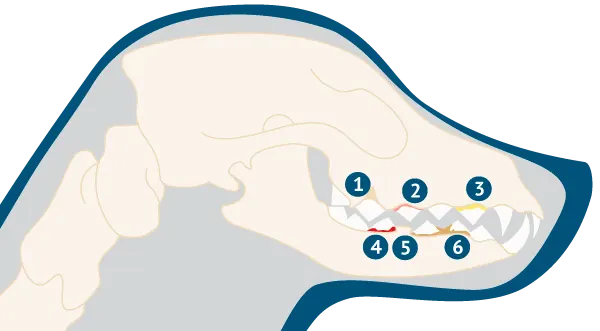
- Exposed tooth neck
- Swollen gums
- Pus formation
- Gum bleeding
- Tooth loss
- Tartar
Off to the Veterinarian
If one or more of these symptoms occur, you should visit a veterinarian as soon as possible. Gum inflammation usually does not heal on its own. On the contrary, if the inflammation is not treated, severe conditions such as destruction of the tooth-supporting apparatus and gum recession can result. If bacteria spread from the mouth to the rest of the body, your dog’s organs are also at risk. Therefore, do not delay the veterinarian visit!
Fortunately, you don’t have to worry about the costs, thanks to pet health insurance. It covers veterinary costs if inflamed gums and possible subsequent illnesses need treatment. Some dog insurance policies even contribute to dental prophylaxis!
Causes of Gum Inflammation in Dogs
Gum inflammation is not uncommon in dogs. Over 80% of all dogs experience it at least once in their lives. Various factors lead to such an infection. Here’s an overview:
- Food residues, tartar, and bacterial plaque: An unhealthy oral flora and poor dental hygiene are considered the main causes of gum inflammation in dogs.
- Often, a small injury to the gum is also the trigger.
- Tumors in soft oral tissue can also be the cause.
- Eating feces! This is not only disgusting but often a sign of malnutrition. Both ingested feces and malnutrition can lead to gum inflammation.
- Tooth misalignments, fungal infections, and autoimmune diseases are other possible causes.
Treatment: How to Combat Gum Inflammation in Dogs
If your dog is suffering from gum inflammation, only a visit to the veterinarian can help. And do it as soon as possible. The longer you wait, the more challenging the treatment becomes. Your vet will first determine the degree of infection and conduct a thorough investigation into the causes. Only then will they know which therapy is appropriate.
Anti-Inflammatory Agents and Antibiotics
If your dog’s gums are only slightly red and swollen, the entire oral cavity is moistened with an anti-inflammatory solution. If necessary, the veterinarian may also prescribe antibiotics that you administer to your furry friend for several days.
Professional Dental Cleaning
If tartar and/or plaque are responsible for gingivitis in dogs, only professional dental cleaning can help. This involves a complete under-anesthesia restoration of your pet’s teeth and gums. Most veterinarians use an ultrasonic cleaner and polish the teeth afterward with a paste. Subsequently, the gum pockets are cleaned with a special rinse of saline solution and chlorhexidine. A multi-day antibiotic therapy is routine after such a procedure, especially if the bacteria have already spread throughout the dog’s body.
Tooth Extraction
In advanced gingivitis, all teeth are often removed, especially if most teeth are already loose and tooth necks are exposed. The goal of tooth extraction is to prevent further inflammation.
Natural Remedies
If your dog suffers from chronic gum inflammation, supplementing the therapy with natural medicine is advisable. Homeopathic remedies, laser therapy, and phytotherapy enhance your pet’s immune system and self-healing abilities.
Home Remedies
While home remedies like lukewarm chamomile tea alleviate the symptoms of gingivitis in dogs, they do not address the root cause. A visit to the vet is still urgently necessary. Home remedies alone will not effectively manage the inflammation.
Important:
Relying solely on your veterinarian’s treatment is not sufficient for successfully combating gum inflammation in your dog in the long run. Studies show that healthy oral and dental care is crucial.
Preventing Gum Inflammation in Dogs
To avoid inflammation altogether, take the following preventive measures:
- Regular Toothbrushing: Ideally, introduce your furry friend to toothbrushing as early as possible. In pet stores, you can find a wide range of dog toothbrushes and toothpaste with chicken flavor, making dental care more enjoyable for your canine companion. Learn more about how to brush your dog’s teeth here.
- Feed Your Dog Dental Care Snacks: These stimulate saliva flow and encourage chewing, preventing unwanted plaque buildup. Treat your furry friend to dental chews more often.
- Barf Diet: Raw feeding is the ultimate diet for preventing gum inflammation in dogs. This diet avoids sugar and grains.
- Veterinary Dental Prophylaxis: Your veterinarian should inspect your dog’s mouth at least once a year. Damaging deposits that could cause gum inflammation are thus recognized and eliminated promptly.
- Avoid Unsuitable Toys: Keep away from inappropriate toys! Tennis balls and sharp objects like sticks have no place in your dog’s mouth. They can be dangerous, causing infections. Opt for chew toys instead, ensuring they can withstand your furry friend’s bites.
Conclusion: Gum Inflammation in Dogs
Dogs are particularly susceptible to gum inflammation. You can prevent it by following the tips mentioned above. However, the risk of gingivitis remains. Therefore, closely observe your furry friend, allowing you to identify signs of inflammation early. Regular preventive check-ups with your dog will spare them from a painful disease progression and lengthy treatment.
When Gum Inflammation Becomes a Struggle – Pet Health Insurance
You should not take gum inflammation lightly. The further the infection progresses, the more painful and dangerous it becomes for your dog. A visit to the veterinarian is mandatory. How about getting pet health insurance? It covers veterinary costs if your furry friend needs treatment or surgery. This way, you are well protected.